Find out everything you need to know about Apple Lossless Audio
Apple Music Lossless Audio
On May 17th 2021, Apple announced that from June 2021 they would begin offering lossless audio via their Apple Music streaming service. Access to lossless audio comes at no extra cost to an existing subscription, with CD-quality audio available across its entire library and hi-resolution streaming on over 70 million songs.
Prior to this, Apple Music had only offered ‘lossy’ compressed audio - a compressed format which is much easier for distribution. Audiophiles had previously been forced to use alternative services such as Tidal and Amazon Music Unlimited, often paying an additional fee for access to hi-res streaming.

What is Lossless Audio?
A lossless audio coding format refers to any compressed version of a sound that can be decoded and played back in its original, uncompressed form. An example of a lossless file type is FLAC format - an open source format.
Uncompressed audio formats refer to those which offer no compression, and are therefore not usually used for storing music due to the increased file size. They are used in professional scenarios - pulse-code modulation (PCM or .wav) is an example of where you might see files in this format, or sometimes as AIFF files on Apple systems. These formats also retain all aspects of the sound quality as they have never been compressed.
A lossy audio coding format refers to audio that has been compressed at the cost of irretrievable data, resulting in lower-resolution representations of the sounds. MP3 files are a lossy format, as are AAC files which Apple had previously used for its streaming service.
Audio files are compressed and decompressed with an audio codec. An example of this is the LAME encoder, regarded as one of the best software encoders for MP3 compression.
What is Apple Lossless Audio Format?
The Apple lossless format is referred to as ALAC (Apple Lossless Audio Codec), and the encoder is sometimes known as ALE (Apple Lossless Encoder).
To better understand lossless, lossy, and uncompressed audio, it helps to know a little about bit depth and sample rate.

Digital Audio, Bit Depth and Sample Rate
Digital audio refers to the ways in which computer systems can store and recreate audio information. Analog sound waves must have certain characteristics captured and then converted into a format which software can process in order for us to manage audio on a computer.
The sample rate of an audio file is concerned with how frequently a sample of the sound is captured by the computer - this graph shows how a higher sample rate will capture a sound wave more accurately than a lower sample rate would be able to.
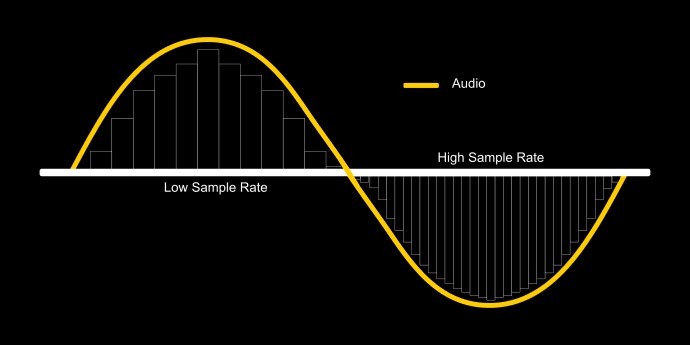
Sample rate is measured in kilohertz (kHz) - for example, CD-quality audio is played at a sample rate of 44.1kHz. Human hearing tends to start around 20Hz, and goes up to around 20kHz - so a sample rate of more than double this range should ensure that the entire frequency range audible to humans is captured sufficiently. However, to avoid digital artefacts and what is known as ‘aliasing’, professionals often use higher sample rates until the final bounce of a project for the consumer.
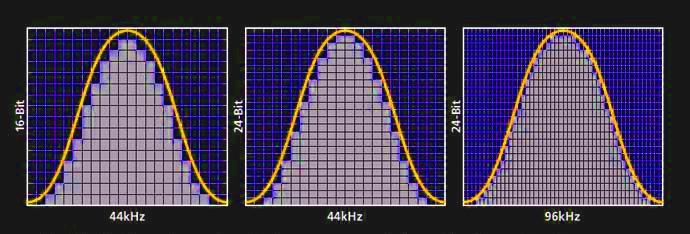
The audio bit depth of a digital sound is the finite number used to determine the amplitude of each wave per sample. A higher bit depth will allow for more amplitude values to be allocated to each sample:
16-bit: 65,536 values
24-bit: 16,777,216 values
32-bit: 4,294,967,296 values
In this illustration it is clear to see how a higher bit depth is able to express a more true representation of the original sound - and how the increased sample rate improves this digital representation further.
Streaming Lossless with Apple Music
In order to get the best-quality listening experience from Apple Music there are some important things to remember..
1. Bluetooth
Although Apple has been keen to innovate in the world of wireless headphones (even going as far as to remove 3.5mm headphone connectivity from its iPhone models), the streaming of lossless audio is impossible over Bluetooth. Check out our range of high-end headphones for some audiophile approved options.
2. Apple Dongle
Apple dongles do not support greater than 24-bit/44.1kHz audio. Whilst this is regarded as hi-res audio in terms of bit depth, the sample rate is equal to that of CD and other consumer-quality audio formats, meaning that some songs and pieces of music will not be heard in their true lossless form.
3. Digital-to-Analog Converters
To combat this and hear audio with a sample rate of up to 192kHz, you will need a digital-to-analog converter - otherwise known as a ‘DAC’. This will ensure that no downsampling occurs and the most true representation of the sound is delivered to your headphones or monitors!
4. Sample Rate Switching
Whilst iPhone and iPad will utilise automatic sample rate switching in order to deliver the optimum audio resolution, this is not the case on Mac OS. Users must enable increased bit depth and sample rate playback in order to avoid downsampling and hear true lossless audio.
For Musicians
Now that lossless streaming is available to everyone, musicians should be excited! Gone are the days of people hearing badly compressed versions of your songs imported into iTunes - at the click of a button the world can hear your music in glorious hi-resolution, just the way you intended for it to be heard.
If you want to make sure your recording process allows for every beautifully crisp detail to be heard, check out our outstanding range of Studio Equipment and Recording Gear. Kit yourself out with a high-end microphone or a new interface, and read through our Home Recording Buying Guide to ensure you get the perfect setup for hi-resolution recording! We even have Studio Package deals so that you won’t forget any important accessories and can get fully equipped on a budget.
If you’re still not sure what you need, come along to your local PMT store and talk to one of our Experts, or call us on 0151 448 2089 and find out everything there is to know about Lossless Audio!




